Nature, in itself, is a hub of life and array of useful resources that we humans can sincerely draw from.
In this article, we will briefly look into the philosophy, principles, and problems of Natural Farming.
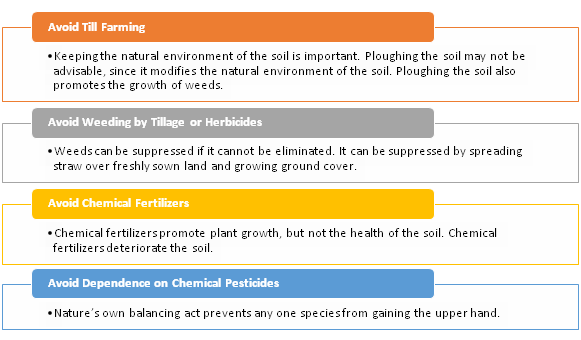
The root philosophy of natural farming was and is to allow nature to produce healthy food, keep ourselves and the land healthy. Natural farming is a natural phenomenon with little intervention or even no intervention of human efforts. The farmer, in this context, plays a facilitator’s role. And nature does its work on its own.
The essence of natural farming is in minimizing external inputs to the farmland. It is a belief that nature has a way of taking care of us when we do not destroy its natural instincts.
What can you expect from this article?
- Natural Farming and it’s Central Principles
- The basic difference between natural farming and organic farming
- Interesting techniques of natural farming in India
- Status of natural farming in India
- Challenges of natural farming
Natural Farming and its central principles
On the other hand, Masanobu Fukuoku, a well-known practitioner of natural farming, hailing from Japan, has proven track record for over 50 years in developing nature’s principles of farming. You can read more about his natural farming story in his book “The One-Straw Revolution”.
The essence of natural farming is in minimizing external inputs to the farmland. Nature has a way of taking care of us when we do not destroy its natural instincts.
What are the basic differences between natural farming and organic farming?
Natural farming is quite different from organic farming. Very less or none of the application of fertilizers or pesticides or herbicides is practiced in natural farming. We can confidently say that human labor counts to about 20% out of 100, while 80% goes under nature’s care on taking care of the farm. It is also called as ‘do nothing’ farming. It is an environmentally sustainable way of increasing food, primarily built on the relationship between the farmer, land, and nature.
[vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_custom_heading text=”Natural Farming” font_container=”tag:h3|text_align:center”][vc_column_text]- Eliminates all the components of modern farming
- Practices “do nothing” approach
- Believes in ‘no cultivation’, ‘no chemical fertilizers’, no weeding’ and ‘no plant protection’
- Includes all the components of modern farming
- Focuses on a soil-building program, highly intensive natural farming
- Believes in maintaining a living soil, retaining all essential nutrients, and organic mulching.
Other interesting techniques of Natural Farming in India
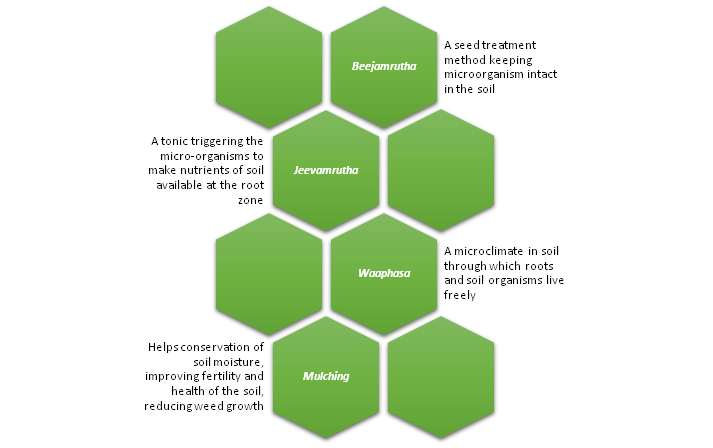
For thousands of years, farmers and agriculturists in India have been practicing natural farming.
‘Rishi Kheti’ is another name for it in India. Rishi Kheti draws its root from ancient Vedic principles of farming such as the use of animal waste and herbal juices for controlling pests and promoting the growth of plants.
Agrarian crisis still persists in the Indian economy, being a grave threat to small-scale farmers. Privatization, a high rate of interest on agriculture loan, and inaccessible markets have had its share on increasing the cost of seeds and making it tough for farmers. These implications have led farmers to commit suicide.
How have modern agricultural practices impacted the environment?
There have been dramatic climate changes, genetic engineering, pollutants, deforestation, irrigation problems, soil degradation, and waste. Plus, air, water, and soil quality have been reduced as a result of excessive use of fertilizers such as urea, phosphorus, and nitrate along with several other pesticides.
Inorganic chemical fertilizers and pesticides and their enormous usage have brought-in contamination of groundwater, soil, and surface.
The application of pesticides has even given rise to killing plants, fish, birds and other wildlife. The overuse of herbicides on genetically engineered crops leads to nurturing weeds which are herbicide-resistant.
On the other hand, the Indian economy continues to face agricultural transformation. Yet, it has been under the mercies of factors such as low sustainability, less agricultural prices, scarcity of water, low demand for agricultural products, low growth of farm productivity, inadequate employment opportunities for agriculturists and so on.
What are the common challenges of Natural Farming?
- It is a draggy gradual process
As mentioned earlier, the concept of natural farming revolves chiefly around the farmer and his land, crops or livestock. In this context, time plays a dominant role in orchestrating the entire natural phenomenon of farming. Also, there is a high level of faithfulness, patience, commitment, and hard work required by the farmer with respect to his relationship with nature’s ways of doing things.
The farmer’s key role here would be:
- To ensure crops are free of pest and diseases, and to use natural methods to stop it.
- To use natural methods to control weeds as well.
- To spend quality time observing and catering to the needs of his crops and animals with diligence in a natural way
Hence, this process is naturally time-consuming due to intensive labor contribution and engagement with the farm which is timeless; unlike the chemical-dependent agriculture or conventional farming methods with lesser labor involvement.
- Don’t expect a high level of productivity in the initial stage
The productivity level would be lesser with natural farming during the initial days. Since there are no big inputs such as machinery and chemicals in natural farming, it is safe to have short term benefits with lesser productivity.
With regard to conventional farming, the numbers on production are comparatively higher with the help of chemicals and machinery, and as a result, the productivity rate is also huge. But with natural farming, initial productivity is less.
- Requires determined agricultural passion mixed with a high sense of reliability on nature
When compared with chemical or mechanical agriculture, the skills expected on the field in natural farming is trickier and indefinite. Depending on nature’s response to the production process, farmers are expected to observe and act accordingly.
Natural farming tends to rely on long-term stable agriculture solutions. In this frame of understanding, it is only wise to carefully observe and act on the production process as per how nature responds to the yield.
So, there is a significant study that needs to be done by the farmer to calculate the cause and effect of the ecosystem. While he does that, he could even note the duration taken to develop the appropriate skills to build a holistic natural farming methodology. In the process, farmers should seek to increase high and valuable products as well.
- Natural products are quite expensive
Natural foods are the most expensive agricultural produces in the market. Perhaps, this is one of the main reasons why natural farming is not fully supported. Consequently, there are not many people who realize its tremendous benefits.
For instance, when you scout the supermarkets, you will find naturally produced vegetables and fruits cost as much as 20 to 40 percent more than their non-organic equivalent. To further the complication, consumers blindly pay the quoted price.
Exuberant costs could be one of the major issues of naturally produced food products.
- Larger and Irrigated areas may not be a good choice for natural farming
It has been researched that approximately 85 percent of farmers in India own less than 2 ha. Smaller areas are believed to get more profit within a limited period of time. Marginal and small-time farmers, these days, prefer smaller areas. These farmers go with high-value commercial crops yielding more nutrients with good irrigation facilities. When the crop is removed in the initial two years, there is a gradual reduction of soil nutrients. With chemical agriculture, it takes around 4-5 years to achieve full yields. Consequently, it may yield surplus returns as well.
- Does not take advantage of Genetic modification
Genetic modification in natural farming is unheard of. Although it is known to help garner a healthy lifestyle, there is no better scope of genetic modification with natural farming. Genetically engineered technologies assist crops to resist pests and diseases or permit weeds. But natural growers miss out on this merit quite, unfortunately. Farmers who follow convectional farming may imbibe the benefits of genetic modification, that is lacking in natural farming.
- The difficulty in managing weed, insect pests and diseases
It is close to the impossibility to control a crop when it gets affected by any pest or disease, in a natural way. Nature falls short in taking immediate action against pest and diseases once it gets hit by them. There are very limited effective and safe pest control options available in natural farming. To add on, there are very few or almost none of the set standard pest and disease management practices.
In conclusion:
Natural farming is one of the best ways to cultivate natural crops and livestock. It is much healthier than the chemicalized version of farming or even mechanized version of it.
One of the main objectives of natural farming in India is to develop a sustainable agriculture system for guaranteed adequate food production in the foreseeable future. Followed by developing self-sufficient agriculture system and developing an alternative strategy over chemical farming.
Natural farming can be pursued still if it can battle against factors such as sinking water slabs, diminishing soil fertility, poor returns to farmers, and increasing costs.

